Aquatic Biomes Chart
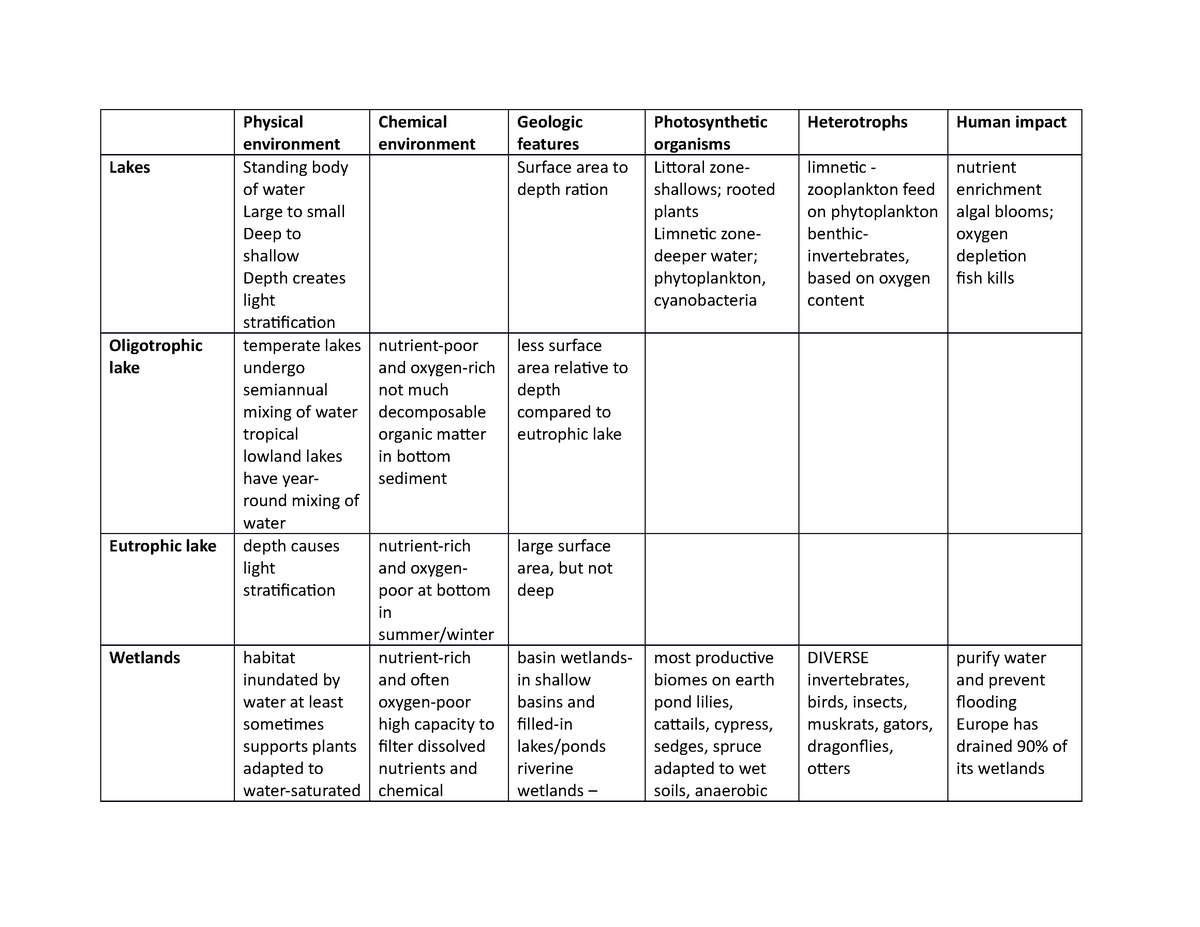
Aquatic Biomes Chart - Typically, freshwater habitats are less than 1 percent salt. The aquatic biome is the largest of all the world's biomes—it occupies about 75 percent of the earth's surface area. Web like terrestrial biomes, aquatic biomes are influenced by abiotic factors. Compare and contrast the characteristics of the ocean zones. In the case of aquatic biomes the abiotic factors include light, temperature, flow regime, and dissolved solids. Freshwater biomes are bodies of water surrounded by land—such as ponds, rivers, and lakes—that have a salt content of less than one percent. Some aquatic biomes are freshwater biomes, where the water contains little or no salt. Humans rely on freshwater biomes to provide aquatic resources for drinking water, crop irrigation, sanitation, and industry. Web aquatic biomes are ecosystems classified by the presence of water (freshwater or marine) and the type of organisms that live in them. The aquatic biome includes the habitats around the world that are dominated by water—from tropical reefs to brackish mangroves, to arctic lakes. Marine life, however, has to be adapted to living in a habitat with a high concentration of salt. Freshwater biomes include ponds, lakes, streams, and rivers, and are a vital source of drinking water. Typically, freshwater habitats are less than 1 percent salt. Freshwater biomes include lakes, ponds, rivers, and streams. Web like terrestrial biomes, aquatic biomes are influenced by. Abiotic factors influencing aquatic biomes. The aquatic medium—water— has different physical and. Summarize the characteristics of standing water and flowing water freshwater biomes. Web aquatic ecosystems include both saltwater and freshwater biomes. Web the aquatic biome is the largest of all the biomes, covering about 75 percent of earth’s surface. Typically, freshwater habitats are less than 1 percent salt. Summarize the characteristics of standing water and flowing water freshwater biomes. The aquatic medium—water— has different physical and chemical properties than air, however. Marine biomes include the ocean, coral reefs, and estuaries. Web updated on march 16, 2019. The aquatic biome includes the habitats around the world that are dominated by water—from tropical reefs to brackish mangroves, to arctic lakes. The aquatic biome is the largest of all the world's biomes—it occupies about 75 percent of the earth's surface area. Web like terrestrial biomes, aquatic biomes are influenced by abiotic factors. Even if the water in a pond. Web freshwater biomes include lakes and ponds (standing water) as well as rivers and streams (flowing water). Aquatic biome information organized into a helpful chart, dr. The aquatic medium—water— has different physical and chemical properties than air. Web the aquatic biome is the largest biome on earth, and it covers around 75% of the earth’s surface. Web climate change, global. Some aquatic biomes are freshwater biomes, where the water contains little or no salt. This biome is usually divided into two categories: Humans rely on freshwater biomes to provide aquatic resources for drinking water, crop irrigation, sanitation, and industry. Web describe the effects of abiotic factors on the composition of plant and animal communities in aquatic biomes. Typically, freshwater habitats. Web the aquatic biome is the largest of all the biomes, covering about 75 percent of earth’s surface. Web freshwater biomes include lakes and ponds (standing water) as well as rivers and streams (flowing water). With low salinity in the water, these bodies support a variety of plant and animal life, including fish, amphibians, reptiles, mammals,. Compare and contrast the. Like terrestrial biomes, aquatic biomes are influenced by a series of abiotic factors. Web aquatic biomes are ecosystems classified by the presence of water (freshwater or marine) and the type of organisms that live in them. They also include wetlands, which will be discussed later. The ocean is divided into different zones based on water depth and distance from the. Marine life, however, has to be adapted to living in a habitat with a high concentration of salt. Freshwater biomes include lakes, ponds, rivers, and streams. Typically, freshwater habitats are less than 1 percent salt. In the case of aquatic biomes the abiotic factors include light, temperature, flow regime, and dissolved solids. Freshwater habitats and marine habitats. The aphotic zone, the neritic zone, the oceanic zone, and the benthic realm. Web aquatic ecosystems include both saltwater and freshwater biomes. Summarize the characteristics of standing water and flowing water freshwater biomes. Some aquatic biomes are freshwater biomes, where the water contains little or no salt. Aquatic ecosystems include both saltwater and freshwater biomes. Marine biomes include the ocean, coral reefs, and estuaries. Web like terrestrial biomes, aquatic biomes are influenced by abiotic factors. The ocean is divided into different zones based on water depth and distance from the shoreline. Web describe the effects of abiotic factors on the composition of plant and animal communities in aquatic biomes. It is home to thousands, if not millions, of different species. Even if the water in a pond or other body of water is perfectly clear (there are no suspended particles. Web the aquatic biome is the largest biome on earth, and it covers around 75% of the earth’s surface. The aquatic medium—water— has different physical and chemical properties than air. The aquatic medium—water— has different physical and. Marine life, however, has to be adapted to living in a habitat with a high concentration of salt. Web like terrestrial biomes, aquatic biomes are influenced by abiotic factors. Compare and contrast the characteristics of the ocean zones. Web aquatic biomes are ecosystems classified by the presence of water (freshwater or marine) and the type of organisms that live in them. Web updated on march 16, 2019. The aquatic biome is divided into two categories; Humans rely on freshwater biomes to provide aquatic resources for drinking water, crop irrigation, sanitation, and industry.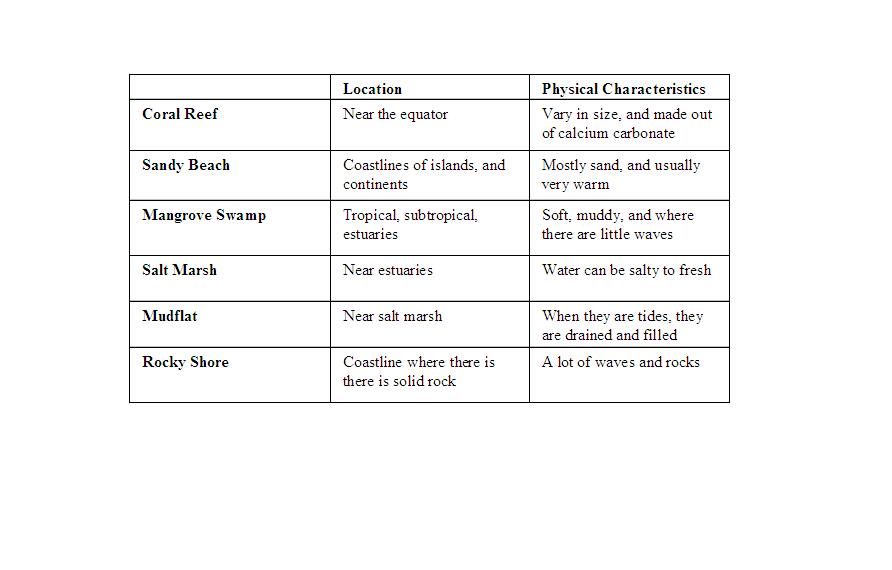
Aquatic Biomes Chart

Aquatic Biomes Chart

Aquatic Biomes Summary Chart
Aquatic Biomes Chart
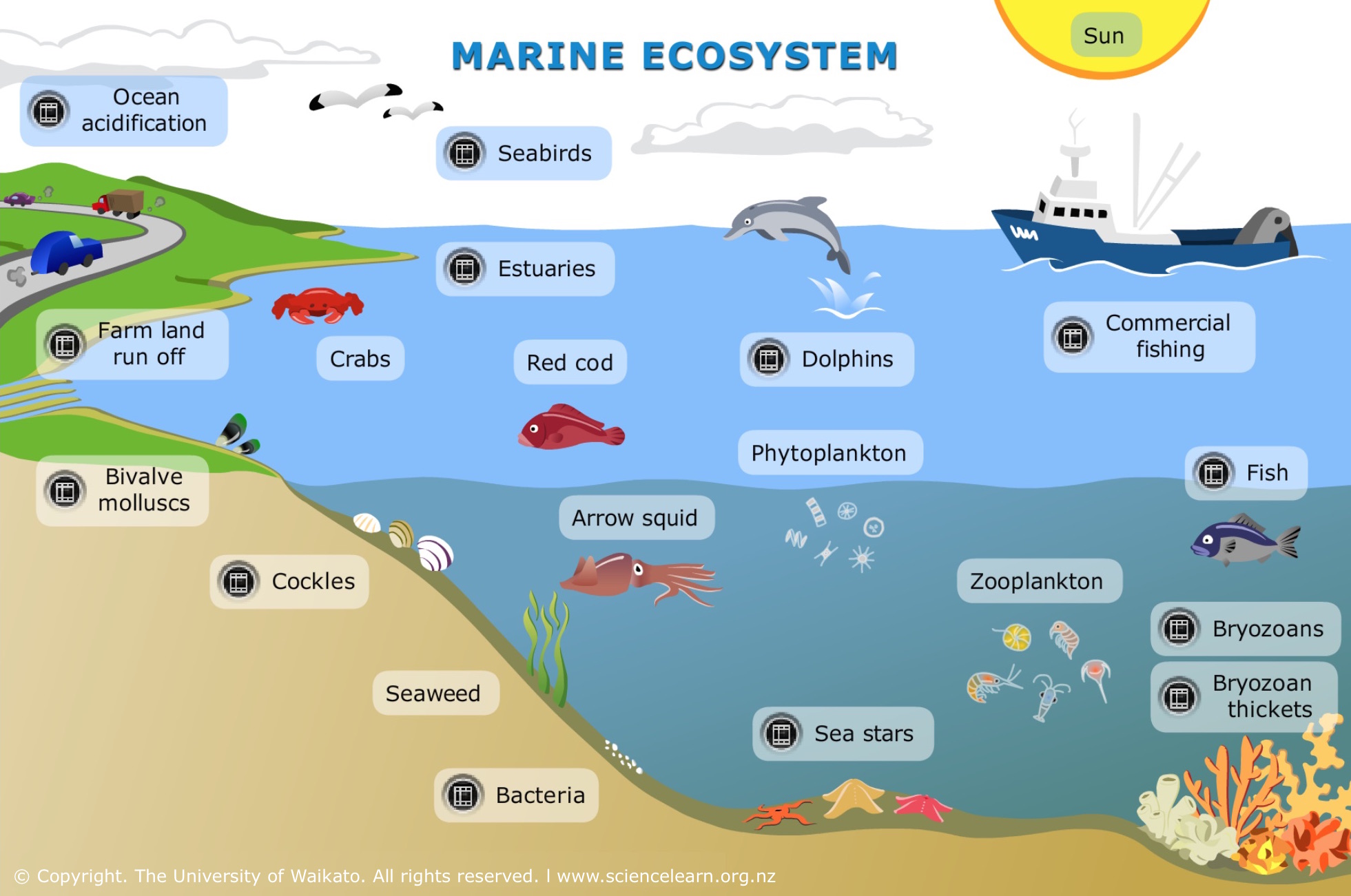
Marine ecosystem — Science Learning Hub

Ch 40.2 Aquatic Biomes Diagram Quizlet

Aquatic Animals Wonderful List of 35 Aquatic Animals for Students
Biomes Chart Oceans Fresh Water

PPT Aquatic Biomes PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1431525
Aquatic Biomes Summary Chart
Web Like Terrestrial Biomes, Aquatic Biomes Are Influenced By A Series Of Abiotic Factors.
Study With Quizlet And Memorize Flashcards Containing Terms Like List The Two Major Aquatic Biomes, List The Three Subcategories Of Freshwater Biomes, List The Three Subcategories Of.
The Aquatic Biome Is The Largest Of All The World's Biomes—It Occupies About 75 Percent Of The Earth's Surface Area.
Web The Aquatic Biome Is The Largest Of All The Biomes, Covering About 75 Percent Of Earth’s Surface.
Related Post:
