An Ice Chart Is Needed To Calculate Kc If
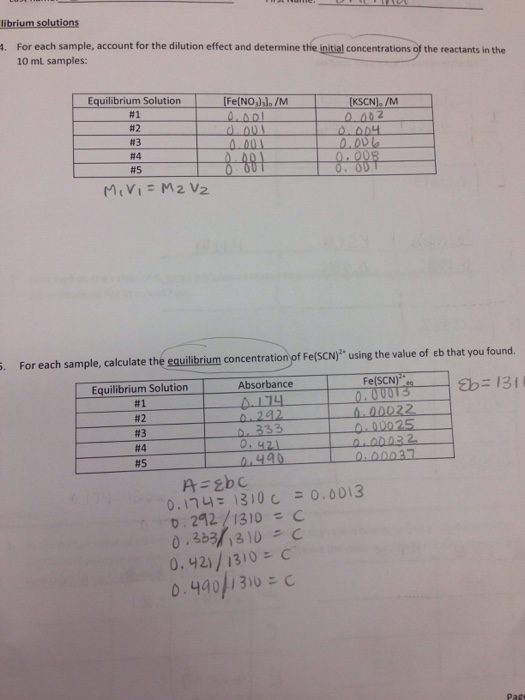
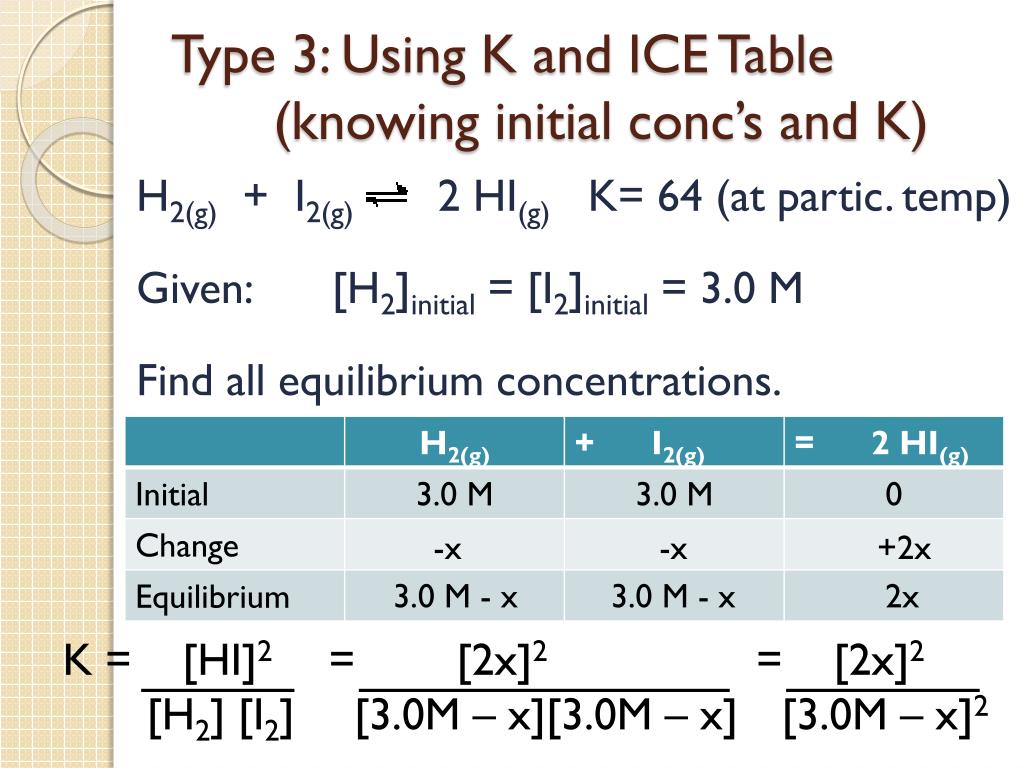
An Ice Chart Is Needed To Calculate Kc If - Web an ice chart is needed to calculate kc if: Consider the reaction and the associated equilibrium constant: 1.6m views 3 years ago new ap & general chemistry video playlist. Web if the initial concentration of bromine is 0.60 molar and the initial concentration of chlorine is also 0.60 molar, our goal is to calculate the equilibrium concentrations of br2, cl2 and brcl. It helps us keep track of the starting concentrations, changes in concentration, and final equilibrium concentrations of the substances involved. Web 1) the rate of a reaction is proportional to the rate of collisions, 2) molecules must collide with a particular orientation if an reaction is to occur, and. Find the equilibrium concentrations from the k value. Select which value to solve for: Now recall that the equilibrium constant k is a ratio of product to reactant amounts at equilibrium. Make an “ice” table, and enter the knowns. Pocl 3 ( g ) ⇌ pocl( g ) + cl 2 ( g ) k c = 0.650 Web 1) the rate of a reaction is proportional to the rate of collisions, 2) molecules must collide with a particular orientation if an reaction is to occur, and. It helps in calculating unknown equilibrium concentrations using known values and the. Web so, let’s see how the reaction quotient is used to determine the equilibrium concentrations. Web an ice chart is needed to calculate kc if: Web ice tables are composed of the concentrations of molecules in solution in different stages of a reaction, and are usually used to calculate the k, or equilibrium constant expression, of a reaction (in some. Web an ice chart is needed to calculate kc if: But they can also be used to organize our information in order to calculate our equilibrium constant. Find the change for the chemical whose final concentration is known. Make an “ice” table, and enter the knowns. Web 1) the rate of a reaction is proportional to the rate of collisions,. 0.5 moles of c are present at equilibrium, determine k c. Pocl 3 ( g ) ⇌ pocl( g ) + cl 2 ( g ) k c = 0.650 Write balanced equation, and expression for kc. 1.0 moles of each a and b 2 are allowed to reach equilibrium at temperature, t. Web this calculator can be used to. By using the concentrations of reactants and products at equilibrium, k c can be determined. Web this calculator can be used to fill in values of an ice table and find the equilibrium constant of the reaction, initial concentration of reactant, and equilibrium concentration of reactant. To help us find the equilibrium concentrations, we're gonna use an ice table, where. Web how to calculate kc and its units with given equilibrium amounts, and how to calculate equilibrium amounts using ice tables when they are not supplied. Select which value to solve for: Web now, ice charts can help us determine equilibrium amounts. Write out the k c expression. Make an “ice” table, and enter the knowns. Pocl 3 ( g ) ⇌ pocl( g ) + cl 2 ( g ) k c = 0.650 This chemistry video tutorial provides a basic introduction into how to solve chemical equilibrium problems. Now recall that the equilibrium constant k is a ratio of product to reactant amounts at equilibrium. It helps us keep track of the starting concentrations,. Find the k value from known equilibrium concentrations. 0.5 moles of c are present at equilibrium, determine k c. Web this video contains the solution to the following question. Web 1) the rate of a reaction is proportional to the rate of collisions, 2) molecules must collide with a particular orientation if an reaction is to occur, and. By using. If the concentration of so3(g) at eq. Assume that the initial concentration of a in each case is 1.0 m and that no b is present at the beginning of the reaction. Web how to calculate kc and its units with given equilibrium amounts, and how to calculate equilibrium amounts using ice tables when they are not supplied. Web this. With an ice chart, we can figure out which way the reaction goes and find the equilibrium constants. Web so, let’s see how the reaction quotient is used to determine the equilibrium concentrations. Web now, ice charts can help us determine equilibrium amounts. 2) find the change in concentration for the species of interest. Web ice tables are composed of. A combination of initial concentrations and at least one equilibrium concentration are given if only equilibrium concentrations are given, we don't need an ice chart to solve for kc, and if only initial concentrations are given, it will be impossible to calculate kc. It helps in calculating unknown equilibrium concentrations using known values and the stoichiometry of the reaction. Web this calculator can be used to fill in values of an ice table and find the equilibrium constant of the reaction, initial concentration of reactant, and equilibrium concentration of reactant. To set up an ice table using the following steps. Select which value to solve for: Web this video contains the solution to the following question. Web ice tables are composed of the concentrations of molecules in solution in different stages of a reaction, and are usually used to calculate the k, or equilibrium constant expression, of a reaction (in some instances, k may be given, and one or more of the concentrations in the table will be the unknown to be solved for). An ice chart is useful to calculate kc when you have either initial, equilibrium, or a combination of concentrations. If the concentration of so3(g) at eq. Write out the k c expression. 3) using stoichiometry find the changes which must have occurred in the other species. A combination of initial concentrations and at least one equilibrium concentration are given if only equilibrium concentrations are given, we don't need an ice chart to solve for kc, and if only initial concentrations are given, it will be impossible to calculate kc. Web how to calculate kc and its units with given equilibrium amounts, and how to calculate equilibrium amounts using ice tables when they are not supplied. To help us find the equilibrium concentrations, we're gonna use an ice table, where i stands for the initial concentration, c stands for the change in. Use stoichiometric relationship to determine the change in concentrations for the others. 1.6m views 3 years ago new ap & general chemistry video playlist.Calculate Kc for each solution, create ICe charts

Solved An ICE chart is needed to calculate Kc if Select the

Chemical Equilibrium Constant K Ice Tables Kp and Kc Membership

An Ice Chart Is Needed To Calculate Kc If

Quadratic Equation ICE Table Equilibrium Calculations YouTube

How To Use Ice Chart Chemistry Best Picture Of Chart
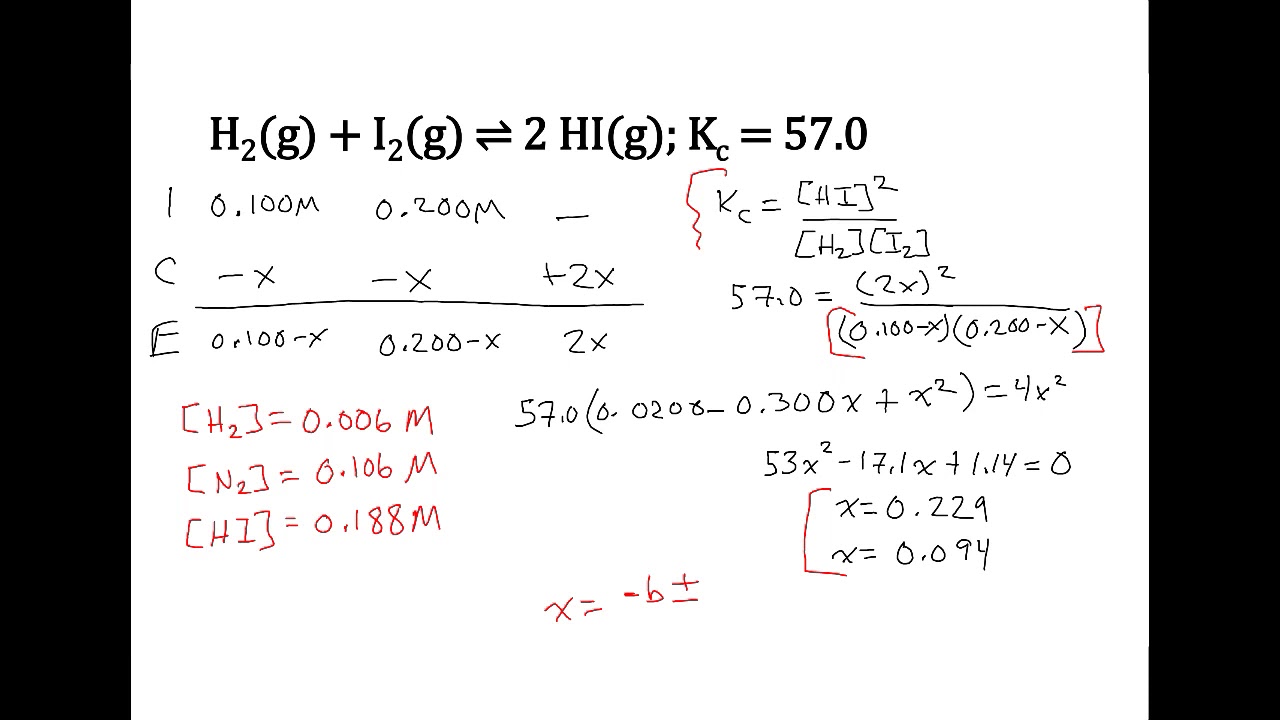
Chemical equilibrium ICE charts YouTube

ICE Table Practice Problems Initial Pressure, Equilibrium Pressure

An Ice Chart Is Needed To Calculate Kc If
PPT The Equilibrium Constant, K, and The Reaction Quotient, Q
Web Now, Ice Charts Can Help Us Determine Equilibrium Amounts.
Web 1) The Rate Of A Reaction Is Proportional To The Rate Of Collisions, 2) Molecules Must Collide With A Particular Orientation If An Reaction Is To Occur, And.
Now, We Recalculate The Equilibrium Concentrations In The Ice Table, Using The Newly Found Value:
Equilibrium Constant ( Kc ) Equilibrium Concentrations.
Related Post: