Aggregate Size Chart
Aggregate Size Chart - Web learn how to classify aggregates based on shape and size, such as coarse and fine aggregates, and their effects on concrete properties. Web table of contents. Find out the sizes of aggregates, such as type 1, type 2 and type 3, and how they. Different types of aggregate, their uses, and sizes. This gravel is often used for paving walk or driveways, at it can be walked and driven on with relative ease. Web size #57 is another of the more popular gravel sizes. Find out the differences between natural and. The gradation uses a set of sieves, and a percentage of crushed rocks should pass through it. Designation given to the smaller aggregate sizes with d less than or equal to 4 mm. Gravel, on the other hand, typically has a very smooth texture and surface because of the natural weathering and wear of being exposed to running water. Gravel, on the other hand, typically has a very smooth texture and surface because of the natural weathering and wear of being exposed to running water. Web table of contents. Sieve and predominantly retained on the 75 μm (no. Find out the differences between natural and. Here is the 304 aggregate base chart. In other words, such a sample has a wide range of particle sizes present in the mix. Designation given to the larger aggregate sizes with d greater or equal to 4 mm and d greater than or equal to 2 mm. Dashed lines indicate limits specified in astm c 33 for fine aggregates and for 25.0 mm (1 in.) coarse. Designation given to the larger aggregate sizes with d greater or equal to 4 mm and d greater than or equal to 2 mm. Designation given to the smaller aggregate sizes with d less than or equal to 4 mm. If you do not know the product density, use the optional density estimator* or contact a local sales representative. Learn. Web learn how to classify aggregates based on shape and size, such as coarse and fine aggregates, and their effects on concrete properties. Sieve and predominantly retained on the 75 μm (no. 200) sieve is called “fine aggregate” or “sand,” and larger aggregate is called “coarse aggregate.”. Web size #57 is another of the more popular gravel sizes. Aggregate gradation. The nominal maximum size of an aggregate specification is defined as the smallest sieve opening through which 100% of the aggregate can pass. Aggregate gradation is of 4 types as explained below: 200) sieve is called “fine aggregate” or “sand,” and larger aggregate is called “coarse aggregate.”. In other words, such a sample has a wide range of particle sizes. Designation given to the larger aggregate sizes with d greater or equal to 4 mm and d greater than or equal to 2 mm. This gravel is often used for paving walk or driveways, at it can be walked and driven on with relative ease. Web learn about the different types of construction aggregates, such as natural, secondary and recycled,. 200) sieve is called “fine aggregate” or “sand,” and larger aggregate is called “coarse aggregate.”. Enter the width, length, thickness, and product density and hit the “calculate” button to calculate your estimate. Designation given to the smaller aggregate sizes with d less than or equal to 4 mm. Web learn how to classify aggregates based on shape and size, such. Gravel, on the other hand, typically has a very smooth texture and surface because of the natural weathering and wear of being exposed to running water. Unlike crushed stone, gravel is usually sold and used in its natural state. This particular size of gravel ranges in diameter from 3/4th of an inch (1.9 centimeters) to 1 inch (2.54 centimeters) in. The chart below is a guide to the stone size range of our gravel and decorative products: Unlike crushed stone, gravel is usually sold and used in its natural state. Description of aggregate in terms of lower (d) and upper (d) sieve sizes (see later text). Web which size gravel stone to choose. Here is the 304 aggregate base chart. Web table of contents. Web this gradation specification is reported on a table or chart (see example below). This gravel is often used for paving walk or driveways, at it can be walked and driven on with relative ease. Description of aggregate in terms of lower (d) and upper (d) sieve sizes (see later text). Gravel, on the other hand,. Description of aggregate in terms of lower (d) and upper (d) sieve sizes (see later text). Web this gradation specification is reported on a table or chart (see example below). Web size #57 is another of the more popular gravel sizes. Designation given to the smaller aggregate sizes with d less than or equal to 4 mm. Find out the sizes of aggregates, such as type 1, type 2 and type 3, and how they. The chart below is a guide to the stone size range of our gravel and decorative products: Sieve and predominantly retained on the 75 μm (no. Dashed lines indicate limits specified in astm c 33 for fine aggregates and for 25.0 mm (1 in.) coarse aggregate. The nominal maximum size of an aggregate specification is defined as the smallest sieve opening through which 100% of the aggregate can pass. Designation given to the larger aggregate sizes with d greater or equal to 4 mm and d greater than or equal to 2 mm. Find out the differences between natural and. 200) sieve is called “fine aggregate” or “sand,” and larger aggregate is called “coarse aggregate.”. This particular size of gravel ranges in diameter from 3/4th of an inch (1.9 centimeters) to 1 inch (2.54 centimeters) in diameter. The gradation uses a set of sieves, and a percentage of crushed rocks should pass through it. Web table of contents. Web which size gravel stone to choose.
Stone And Gravel Size Chart

Sizes of aggregate use in different structures Engineering Society
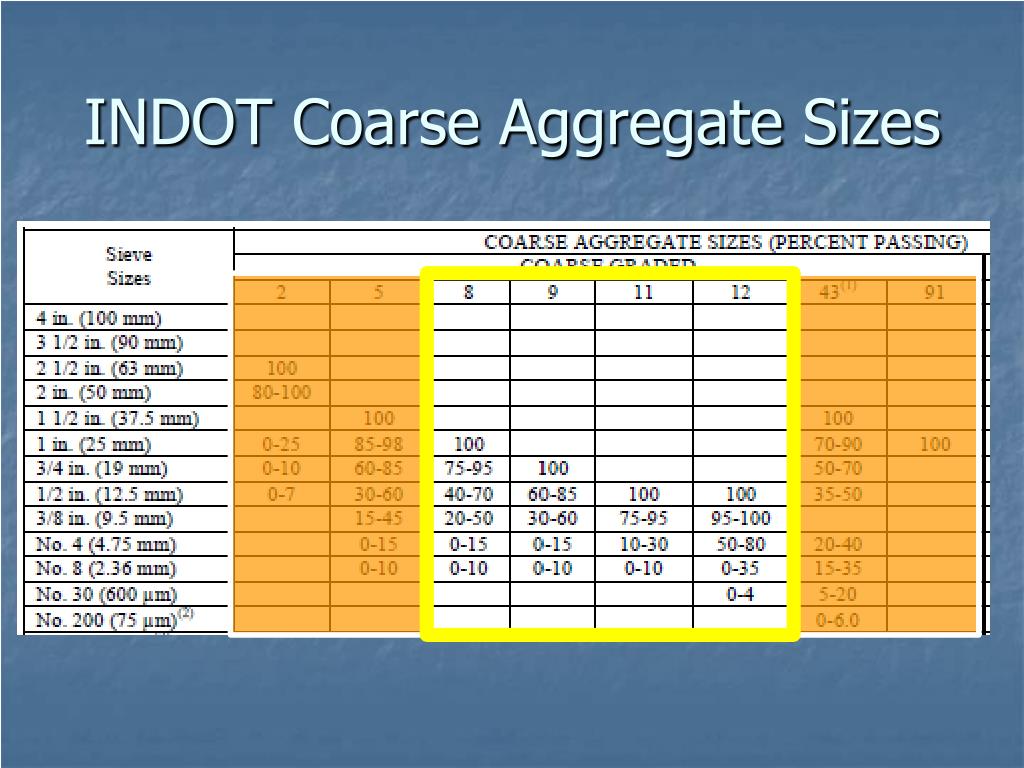
PPT BASICS OF A GOOD ROAD ASPHALT AND AGGREGATES PowerPoint
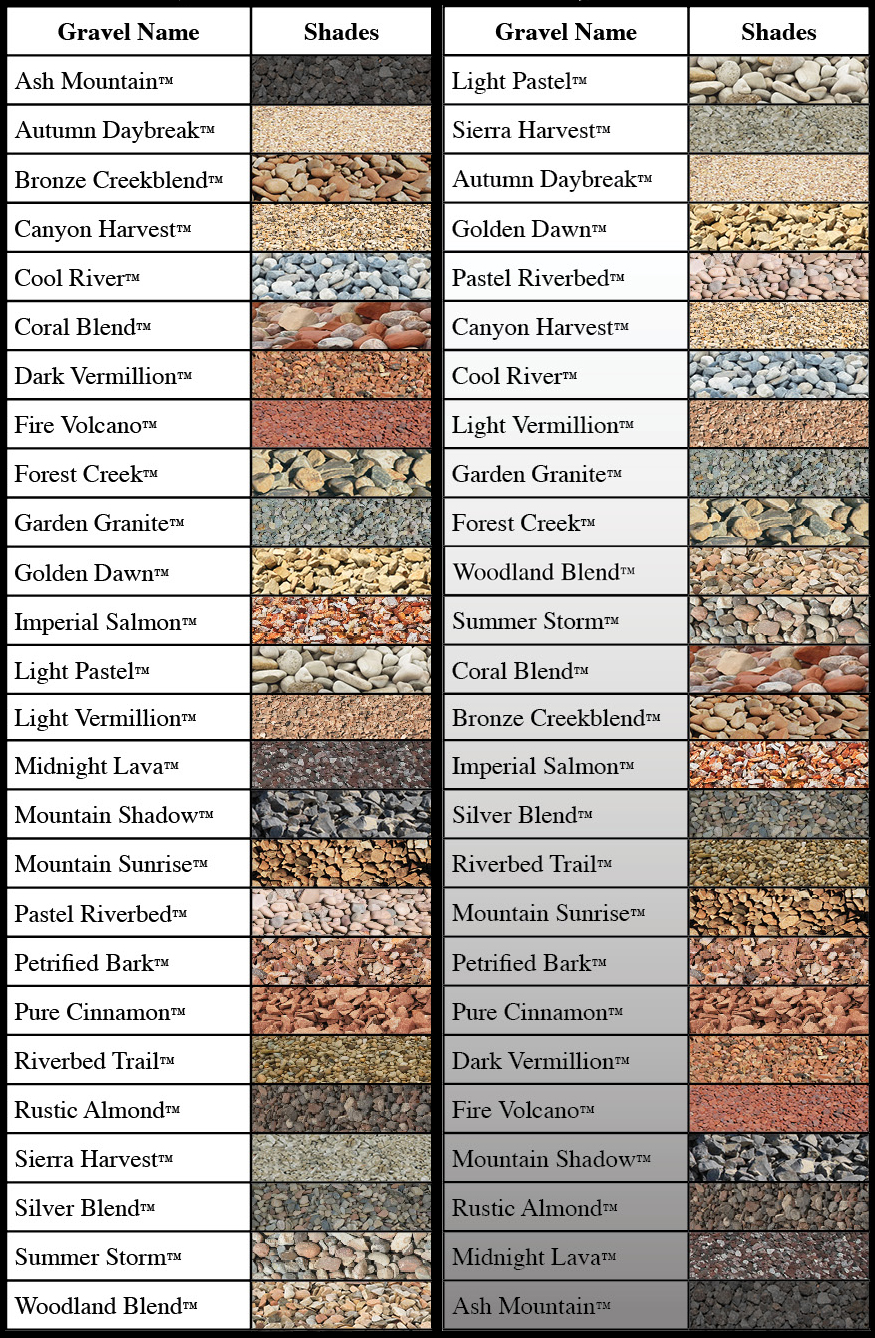
Landscape Rock Size Chart

Aggregate Gravel Size Chart
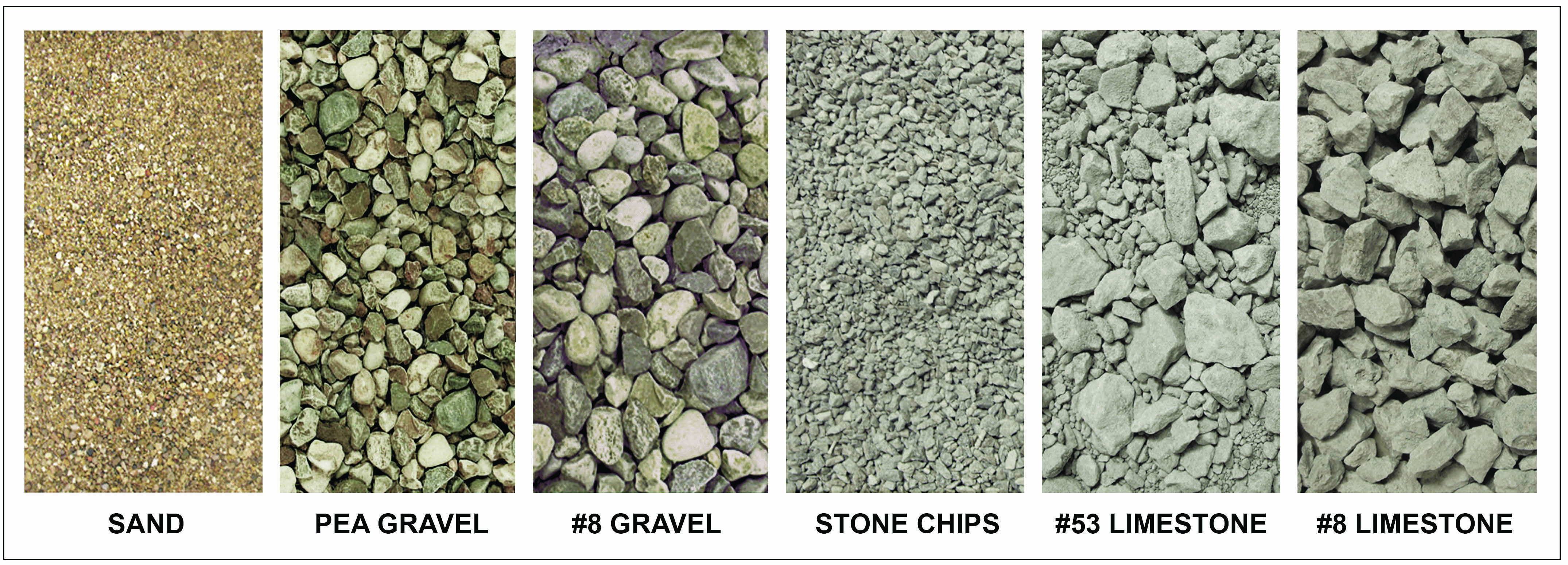

Driveway Gravel Sizes Chart

Concrete Mix for Different Works and Size of Aggregates/Proportion for

Southern Aggregates Size Chart Sign BB Graphics & The Wrap Pros
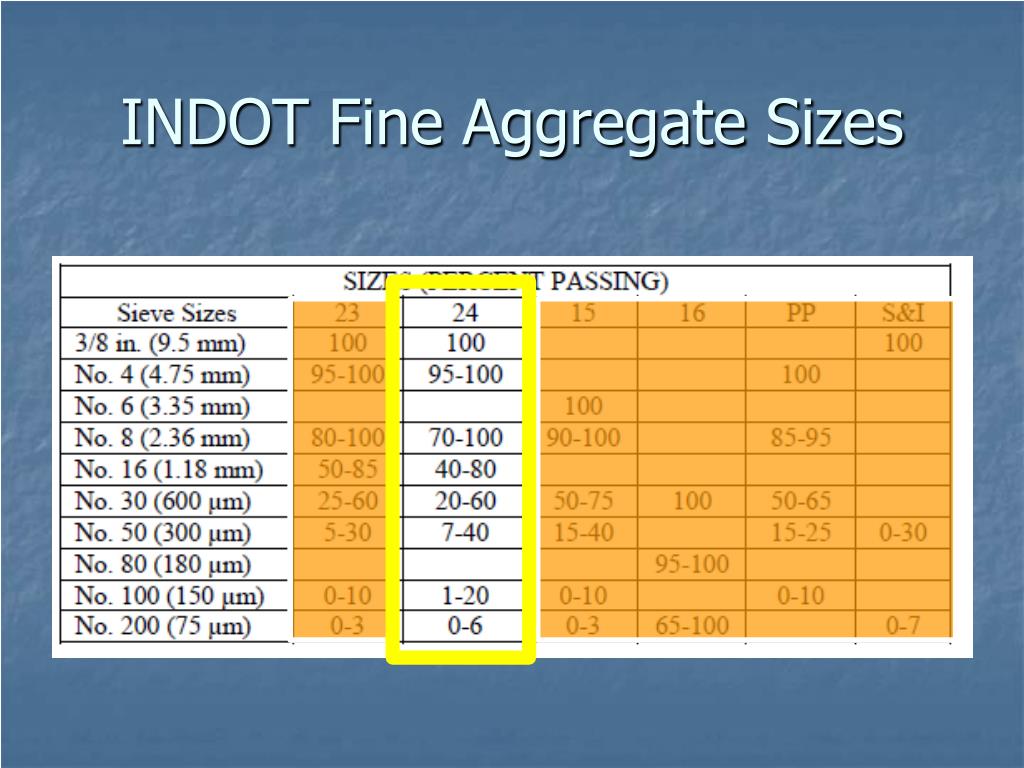
PPT BASICS OF A GOOD ROAD ASPHALT AND AGGREGATES PowerPoint

Pervious concrete mix proportions for size (B) aggregate Download
Learn How To Choose The Right Size Of Crushed Stone Or Gravel For Your Project With This Comprehensive Guide And Chart.
Gravel, On The Other Hand, Typically Has A Very Smooth Texture And Surface Because Of The Natural Weathering And Wear Of Being Exposed To Running Water.
Web Learn About The Different Types Of Construction Aggregates, Such As Natural, Secondary And Recycled, And How They Are Used In Various Applications.
See The Size Variation Of Fine Aggregate And The Chart Of Coarse Aggregate Size Distribution.
Related Post: