4 Types Of Macromolecules Chart
4 Types Of Macromolecules Chart - Nucleic acids (dna, rna) besides their specific roles, carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins can serve as a source of energy, while nucleic acids are the most important macromolecules for the continuity of life. Web proteins are organized at four levels: Synthetic fibers and experimental materials such as carbon nanotubes [2] [3] are also examples of macromolecules. Web as we’ve learned, there are four major classes of biological macromolecules: Web carbohydrates are a major class of biological macromolecules that are an essential part of our diet and provide energy to the body. Web the four types of macromolecules are proteins, lipids, carbohydrates, and nucleic acids. Proteins (polymers of amino acids) carbohydrates (polymers of sugars) lipids (polymers of lipid monomers) nucleic acids (dna and rna; Combined, these molecules make up the majority of a cell’s mass. Web the large molecules necessary for life that are built from smaller organic molecules are called biological macromolecules. Introduction to macromolecules (opens a modal) carbohydrates. Macromolecules are large, complex molecules that are fundamental to both biological and chemical processes. Web the four major types of biomolecules are carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids, and proteins. Web the four types of macromolecules are proteins, lipids, carbohydrates, and nucleic acids. Each is an important cell component and performs a wide array of functions. Web there are four main types. Typically they are constructed from small, repeating units linked together to form this long chain. Browse videos, articles, and exercises by topic. Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. Web there are four major classes of biological macromolecules (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids), and each is an important component of the cell and performs a wide array of functions. Proteins. Typically they are constructed from small, repeating units linked together to form this long chain. Web carbohydrates are a major class of biological macromolecules that are an essential part of our diet and provide energy to the body. Nucleic acids (dna, rna) besides their specific roles, carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins can serve as a source of energy, while nucleic acids. Web there are four main types of macromolecules: If you have any background in nutrition, you will recognize the first three of these as the three standard macronutrients (or macros, in dieting parlance) listed on nutritional information labels. Web carbohydrates are a major class of biological macromolecules that are an essential part of our diet and provide energy to the. Macromolecules are large, complex molecules that are fundamental to both biological and chemical processes. These macromolecules are the building blocks of cells and perform a wide range of functions in living organisms. Web there are four major classes of biological macromolecules (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids); Macromolecules are made up of single units known as monomers that are joined. Synthetic fibers and experimental materials such as carbon nanotubes [2] [3] are also examples of macromolecules. They can have very different shapes, although the most common structure involves a long chain. Web there are four main types of macromolecules: Molecular structure of glucose (opens a modal) dehydration synthesis or a condensation reaction. Web there are four major classes of biological. Polymers of nucleotides) let’s take a closer look at the differences between the difference classes. Combined, these molecules make up the majority of a cell’s dry mass (recall that water makes up the majority of its complete mass). This unit is part of the biology library. Web there are four major classes of biological macromolecules (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic. Nucleic acids are made up of nitrogenous bases, sugars, and phosphate groups, and they carry genetic information. This unit is part of the biology library. These macromolecules are the building blocks of cells and perform a wide range of functions in living organisms. Combined, these molecules make up the majority of a cell’s dry mass (recall that water makes up. Combined, these molecules make up the majority of a cell’s mass. Macromolecules are large, complex molecules that are fundamental to both biological and chemical processes. If you have any background in nutrition, you will recognize the first three of these as the three standard macronutrients (or macros, in dieting parlance) listed on nutritional information labels. The monomers for carbohydrates are. Web there are four major classes of biological macromolecules (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids), and each is an important component of the cell and performs a wide array of functions. Carbohydrates (or polysaccharides), lipids, proteins and nucleic acids. Web carbohydrates are a major class of biological macromolecules that are an essential part of our diet and provide energy to. Proteins (polymers of amino acids) carbohydrates (polymers of sugars) lipids (polymers of lipid monomers) nucleic acids (dna and rna; Each is an important cell component and performs a wide array of functions. Introduction to macromolecules (opens a modal) carbohydrates. Their molecular weights can range from the thousands to the millions. Each is an important cell component and performs a wide array of functions. Web macromolecules are very large molecules. Web there are four main types of macromolecules: Web there are four classes of macromolecules: Web the four types of macromolecules are proteins, lipids, carbohydrates, and nucleic acids. If you have any background in nutrition, you will recognize the first three of these as the three standard macronutrients (or macros, in dieting parlance) listed on nutritional information labels. Primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary. Any change in shape caused by changes in temperature, ph, or chemical exposure may lead to protein denaturation and a. Web the large molecules necessary for life that are built from smaller organic molecules are called biological macromolecules. Web the four major types of biomolecules are carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids, and proteins. Web these are often categorized into four basic types: Biological macromolecules are organic, meaning that they contain carbon.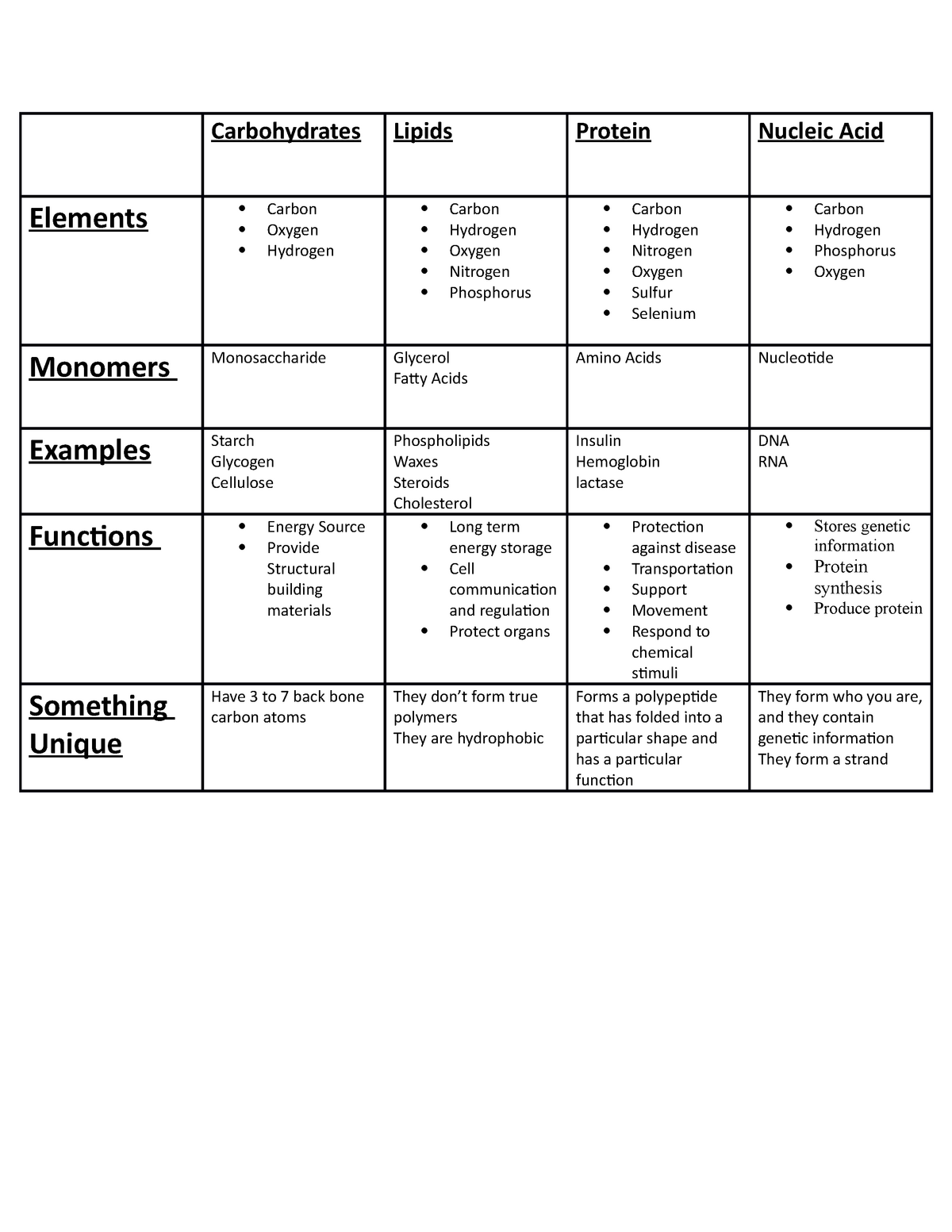
Macromolecules chart Lecture notes A Carbohydrates Elements Carbon
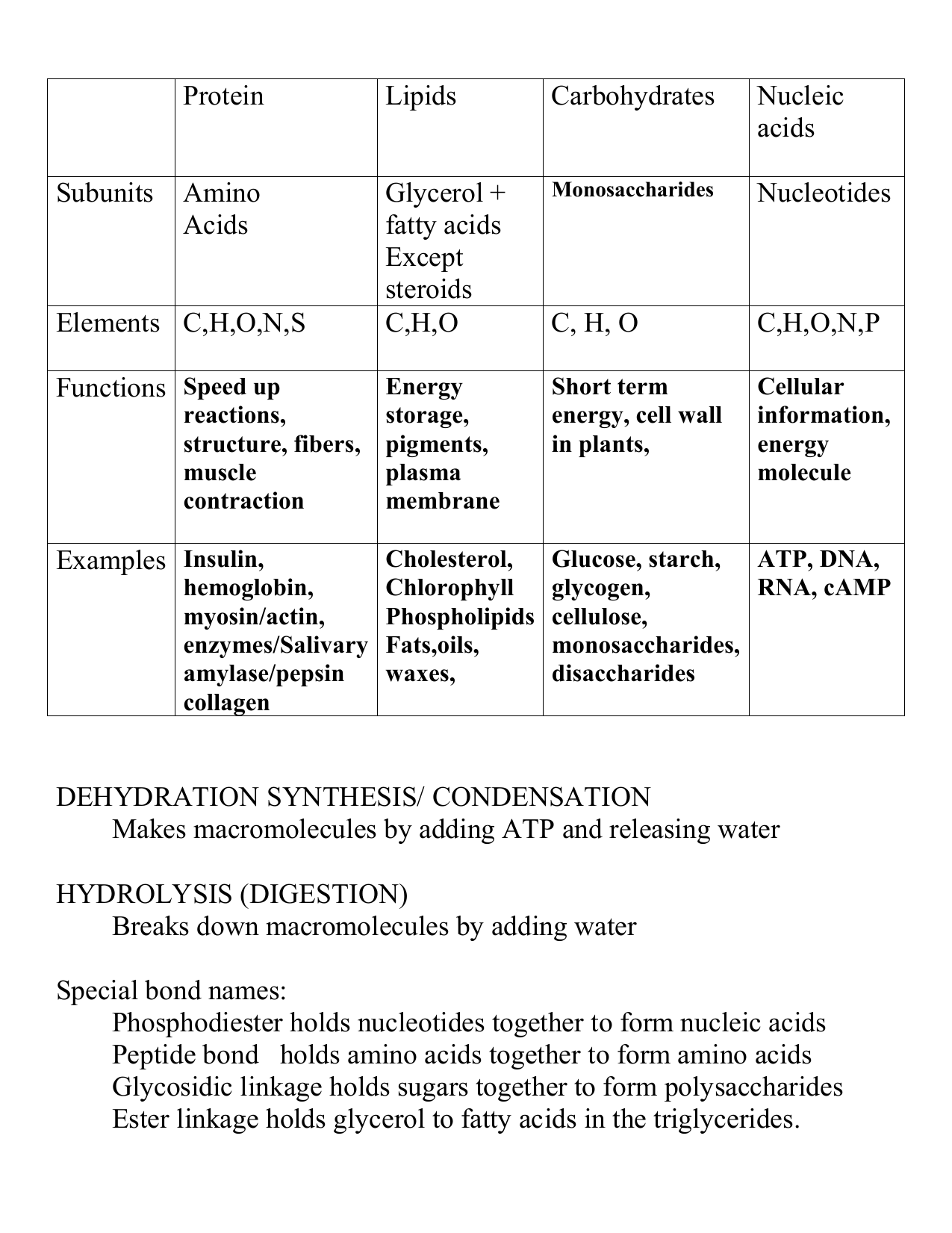
Biochemistry Macromolecules Chart A Visual Reference of Charts Chart

4 types of macromolecules chart Google Search Macromolecules

Pre IB/GT Biology 1 Macromolecules Chart Diagram Quizlet

4 types of macromolecules chart Google Search Macromolecules
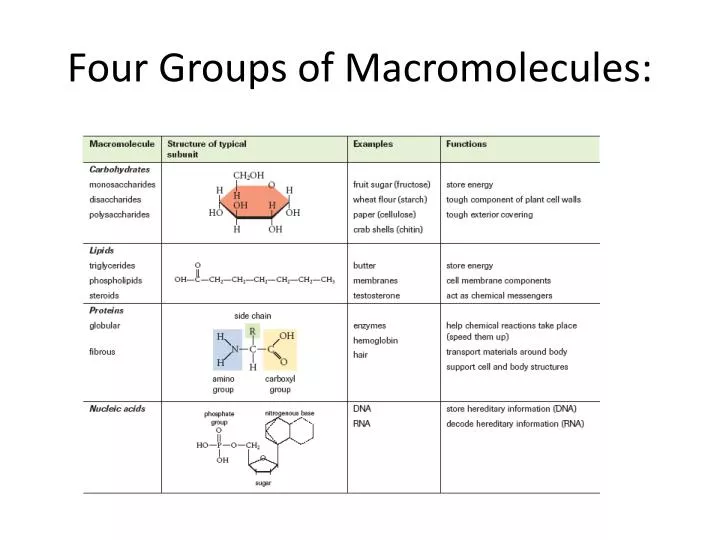
PPT Four Groups of Macromolecules PowerPoint Presentation, free

What Are the 4 Main Macromolecules and Their Functions
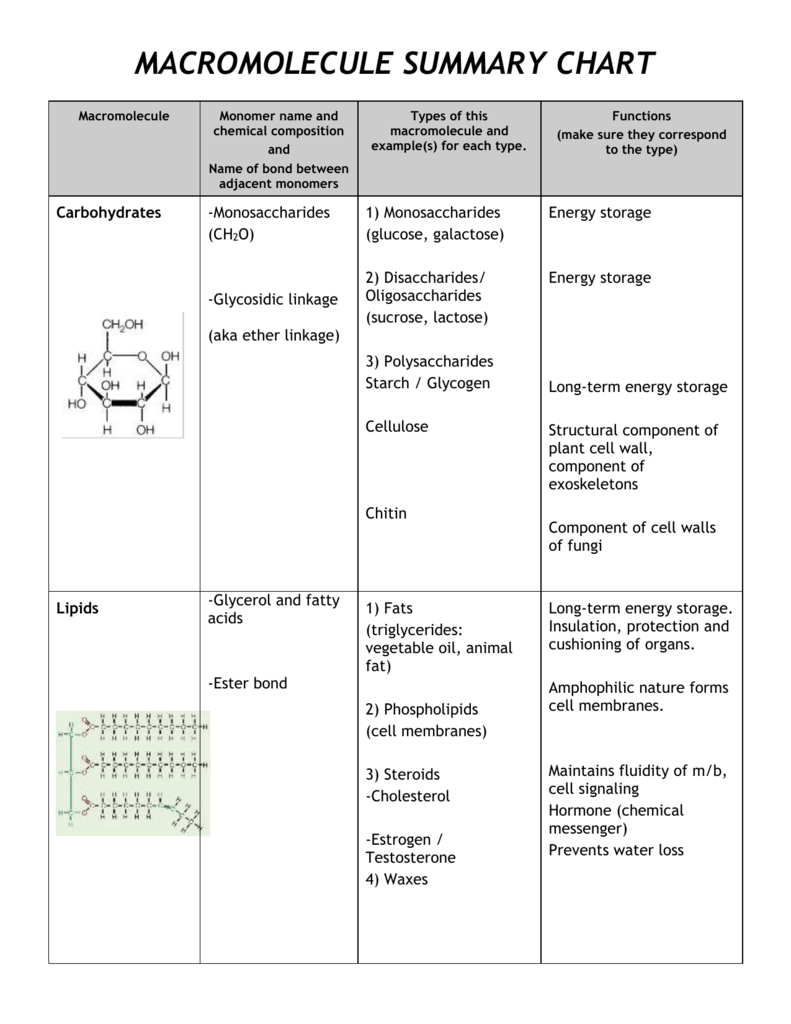
Four Macromolecules Chart

What Are the 4 Main Macromolecules and Their Functions
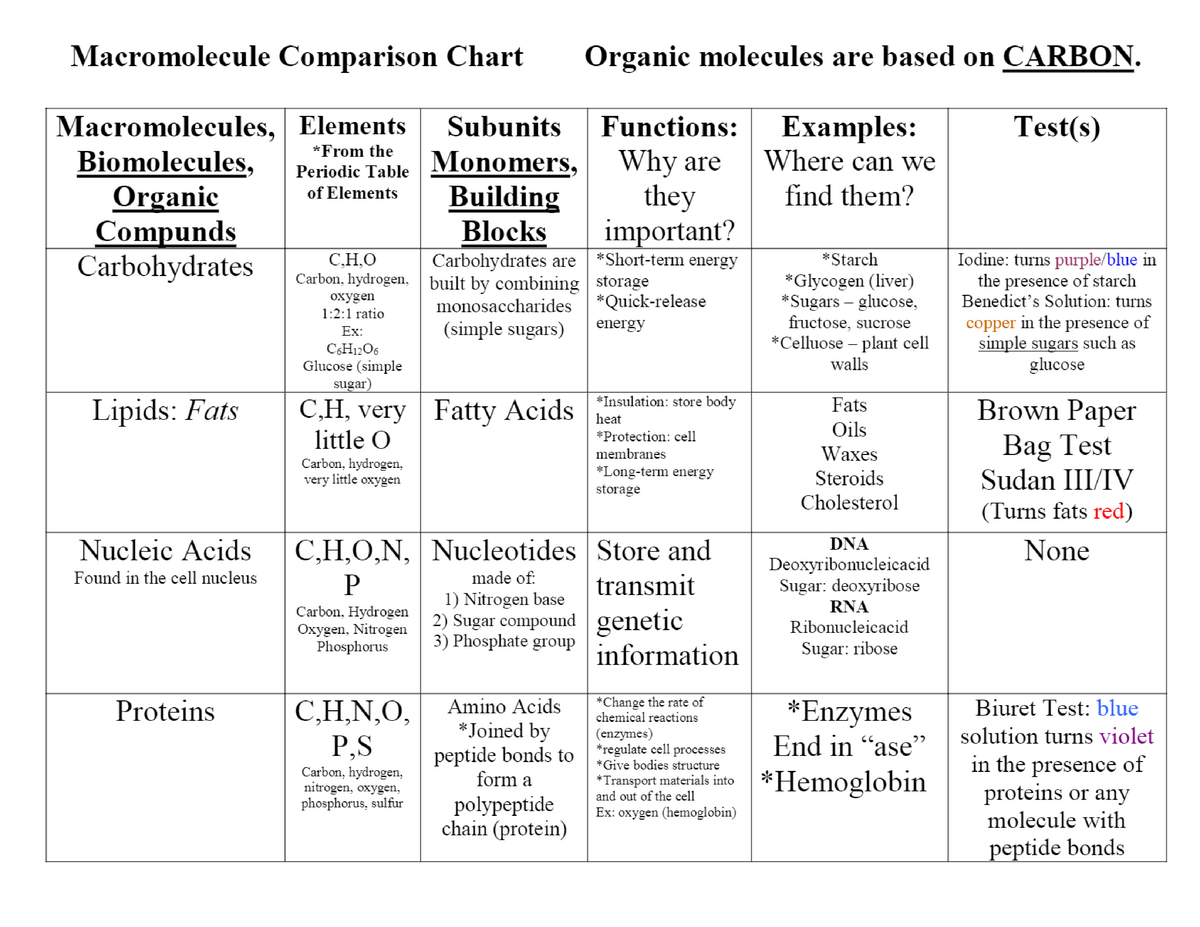
Macromolecule Comparison Chart Organic Bio201 Studocu
There Are Four Major Classes Of Biological Macromolecules (Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins, And Nucleic Acids), And Each Is An Important Component Of The Cell And Performs A Wide Array Of Functions.
Proteins (Polymers Of Amino Acids) Carbohydrates (Polymers Of Sugars) Lipids (Polymers Of Lipid Monomers) Nucleic Acids (Dna And Rna;
Web Biological Macromolecules Are Important Cellular Components And Perform A Wide Array Of Functions Necessary For The Survival And Growth Of Living Organisms.
Macromolecules Are Made Up Of Single Units Known As Monomers That Are Joined By Covalent Bonds To Form Larger Polymers.
Related Post: